SurfaceViewSource
源码位置: frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/SurfaceView.java
surfaceView support scale and translation to its parent or itself
onAttachedToWindow
@Override
protected void onAttachedToWindow() {
super.onAttachedToWindow();
getViewRootImpl().addWindowStoppedCallback(this);
mWindowStopped = false;
mViewVisibility = getVisibility() == VISIBLE;
updateRequestedVisibility();
mAttachedToWindow = true;
mParent.requestTransparentRegion(SurfaceView.this);//main
if (!mGlobalListenersAdded) {
ViewTreeObserver observer = getViewTreeObserver();
observer.addOnScrollChangedListener(mScrollChangedListener);
observer.addOnPreDrawListener(mDrawListener);
mGlobalListenersAdded = true;
}
}
requestTransparentRegion
//ViewGroup
@Override
public void requestTransparentRegion(View child) {
if (child != null) {
child.mPrivateFlags |= View.PFLAG_REQUEST_TRANSPARENT_REGIONS;
if (mParent != null) {
mParent.requestTransparentRegion(this);
}
}
}
@Override//ViewRootImpl
public void requestTransparentRegion(View child) {
// the test below should not fail unless someone is messing with us
checkThread();
if (mView == child) {
mView.mPrivateFlags |= View.PFLAG_REQUEST_TRANSPARENT_REGIONS;
// Need to make sure we re-evaluate the window attributes next
// time around, to ensure the window has the correct format.
mWindowAttributesChanged = true;
mWindowAttributesChangesFlag = 0;
requestLayout();
}
}
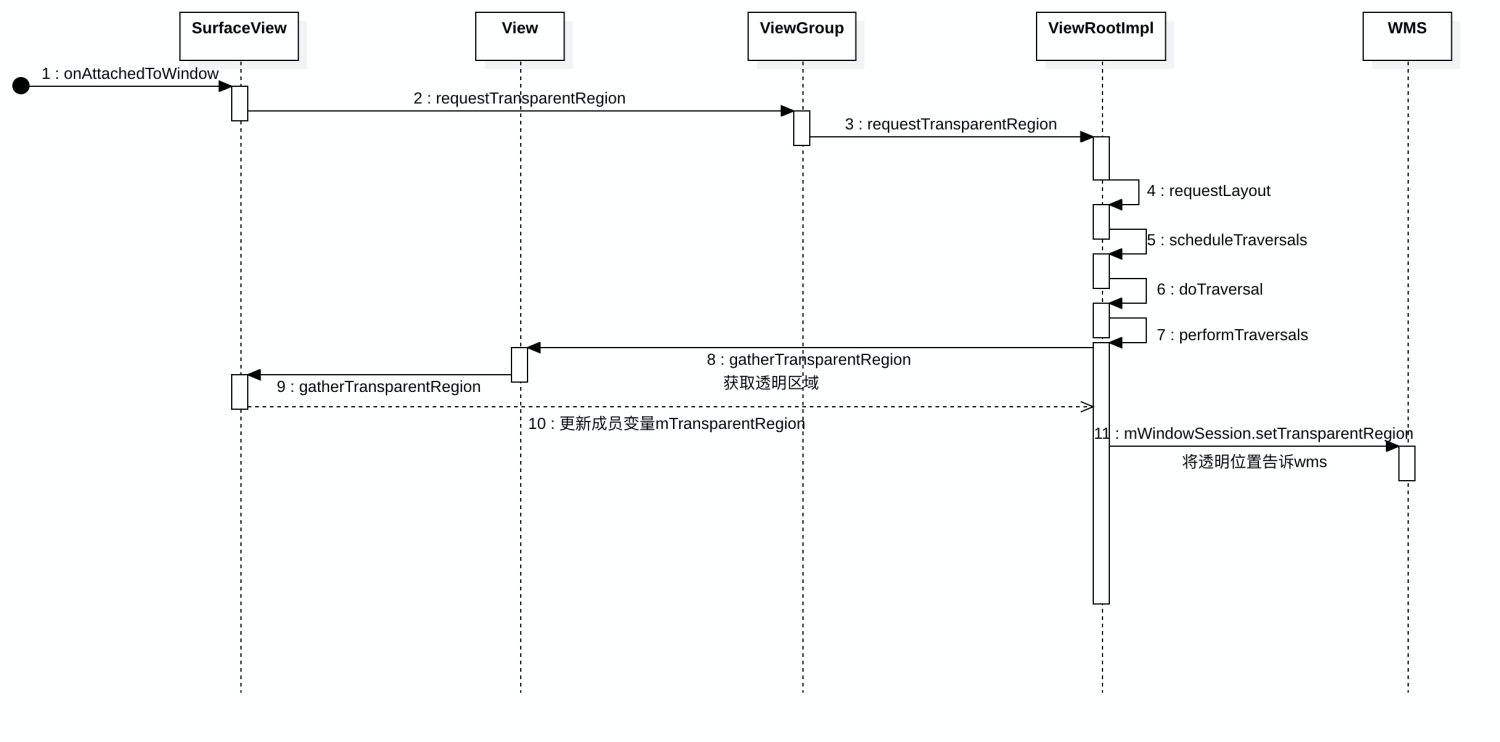
SurfaceView如何挖洞
SurfaceView的窗口类型一般都是TYPE_APPLICATION_MEDIA或者TYPE_APPLICATION_MEDIA_OVERLAY,它的Z轴位置是小于其宿主窗口的Z位置。为了保证SurfaceView的UI是可见的,SurfaceView就需要在其宿主窗口的上面挖一个洞出来,实际上就是在其宿主窗口的绘图表面上设置一块透明区域,以便可以将自己显示出来。 SurfaceView在被附加到宿主窗口之上的时候,会请求在宿主窗口上设置透明区域,而每当其宿主窗口刷新自己的UI的时候,就会将所有嵌入在它里面的SurfaceView所设置的透明区域收集起来,然后再通知WindowManagerService服务为其设置一个总的透明区域。
onWindowVisibilityChanged
@Override
protected void onWindowVisibilityChanged(int visibility) {
super.onWindowVisibilityChanged(visibility);
mWindowVisibility = visibility == VISIBLE;
updateRequestedVisibility();
updateSurface();
}
updateSurface
protected void updateSurface() {
ViewRootImpl viewRoot = getViewRootImpl();
//1 new SurfaceSession
mSurfaceSession = new SurfaceSession(viewRoot.mSurface);
//2 new SurfaceControl
mSurfaceControl = new SurfaceControlWithBackground(
name,
(mSurfaceFlags & SurfaceControl.OPAQUE) != 0,
new SurfaceControl.Builder(mSurfaceSession)
.setSize(mSurfaceWidth, mSurfaceHeight)
.setFormat(mFormat)
.setFlags(mSurfaceFlags));
//3 mSurfaceControl.show()
mSurfaceControl.setLayer(mSubLayer);
if (mViewVisibility) {
mSurfaceControl.show();
} else {
mSurfaceControl.hide();
}
//4 mSurface.copyFrom(mSurfaceControl)
if (creating) {
mSurface.copyFrom(mSurfaceControl);
}
//5 回调SurfaceHolder.Callback, surface的状态变化
if (visible && mSurface.isValid()) {
if (!mSurfaceCreated && (surfaceChanged || visibleChanged)) {
mSurfaceCreated = true;
mIsCreating = true;
if (callbacks == null) {
callbacks = getSurfaceCallbacks();
}
for (SurfaceHolder.Callback c : callbacks) {
c.surfaceCreated(mSurfaceHolder);
}
}
if (creating || formatChanged || sizeChanged
|| visibleChanged || realSizeChanged) {
if (callbacks == null) {
callbacks = getSurfaceCallbacks();
}
for (SurfaceHolder.Callback c : callbacks) {
c.surfaceChanged(mSurfaceHolder, mFormat, myWidth, myHeight);
}
}
if (redrawNeeded) {
if (callbacks == null) {
callbacks = getSurfaceCallbacks();
}
mPendingReportDraws++;
viewRoot.drawPending();
SurfaceCallbackHelper sch =
new SurfaceCallbackHelper(this::onDrawFinished);
sch.dispatchSurfaceRedrawNeededAsync(mSurfaceHolder, callbacks);
}
}
旧版本android系统使用常规View绘制方式通过mSession和WMS通信,并在WMS进程内完成
- new SurfaceSesion (addToDisplay时)
- new SurfaceControl(relayout时)
新版本android9.0,在应用进程内部SurfaceView.UpdateSurface时独立完成了上述流程
/** surfaceView.getHolder
* Return the SurfaceHolder providing access and control over this
* SurfaceView's underlying surface.
*
* @return SurfaceHolder The holder of the surface.
*/
public SurfaceHolder getHolder() {
return mSurfaceHolder;
}
SurfaceHolder.lockCanvas
private final SurfaceHolder mSurfaceHolder = new SurfaceHolder() {
@Override
public void addCallback(Callback callback) {
synchronized (mCallbacks) {
// This is a linear search, but in practice we'll
// have only a couple callbacks, so it doesn't matter.
if (mCallbacks.contains(callback) == false) {
mCallbacks.add(callback);
}
}
}
public Canvas lockCanvas() {
return internalLockCanvas(null, false);
}
final ReentrantLock mSurfaceLock = new ReentrantLock();
final Surface mSurface = new Surface(); // Current surface in use
private Canvas internalLockCanvas(Rect dirty, boolean hardware) {
mSurfaceLock.lock();
Canvas c = null;
if (!mDrawingStopped && mSurfaceControl != null) {
if (hardware) {
c = mSurface.lockHardwareCanvas();
} else {
c = mSurface.lockCanvas(dirty);
}
return c;
}
lockHardwareCanvas
public Canvas lockHardwareCanvas() {
synchronized (mLock) {
checkNotReleasedLocked();
if (mHwuiContext == null) {
mHwuiContext = new HwuiContext(false);
}
return mHwuiContext.lockCanvas(
nativeGetWidth(mNativeObject),
nativeGetHeight(mNativeObject));
}
}
RenderNode.create
HwuiContext(boolean isWideColorGamut) {
mRenderNode = RenderNode.create("HwuiCanvas", null);
mRenderNode.setClipToBounds(false);
mHwuiRenderer = nHwuiCreate(mRenderNode.mNativeRenderNode, mNativeObject,
isWideColorGamut);//mHwuiRenderer在native层就是一个RenderProxy指针
}
new RenderProxy
frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_Surface.cpp
static const JNINativeMethod gSurfaceMethods[] = {
{"nHwuiCreate", "(JJZ)J", (void*) hwui::create },
}
static jlong create(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jlong rootNodePtr, jlong surfacePtr,
jboolean isWideColorGamut) {
RenderNode* rootNode = reinterpret_cast<RenderNode*>(rootNodePtr);
sp<Surface> surface(reinterpret_cast<Surface*>(surfacePtr));
ContextFactory factory;
RenderProxy* proxy = new RenderProxy(false, rootNode, &factory);
proxy->loadSystemProperties();
if (isWideColorGamut) {
proxy->setWideGamut(true);
}
proxy->setSwapBehavior(SwapBehavior::kSwap_discardBuffer);
proxy->initialize(surface);
// Shadows can't be used via this interface, so just set the light source
// to all 0s.
proxy->setup(0, 0, 0);
proxy->setLightCenter((Vector3){0, 0, 0});
return (jlong) proxy;
}
mRenderNode.start
Canvas lockCanvas(int width, int height) {
if (mCanvas != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Surface was already locked!");
}
mCanvas = mRenderNode.start(width, height);
return mCanvas;
}
lockCanvas
public Canvas lockCanvas(Rect inOutDirty)
throws Surface.OutOfResourcesException, IllegalArgumentException {
synchronized (mLock) {
mLockedObject = nativeLockCanvas(mNativeObject, mCanvas, inOutDirty);
return mCanvas;
}
}
SurfaceHolder.unlockCanvasAndPost
public void unlockCanvasAndPost(Canvas canvas) {
mSurface.unlockCanvasAndPost(canvas);
mSurfaceLock.unlock();
}
public void unlockCanvasAndPost(Canvas canvas) {
synchronized (mLock) {
checkNotReleasedLocked();
if (mHwuiContext != null) {
mHwuiContext.unlockAndPost(canvas);
} else {
unlockSwCanvasAndPost(canvas);
}
}
}
mHwuiContext.unlockAndPost
mRenderNode.end(mCanvas);
void unlockAndPost(Canvas canvas) {
if (canvas != mCanvas) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("canvas object must be the same instance that "
+ "was previously returned by lockCanvas");
}
mRenderNode.end(mCanvas);
mCanvas = null;
nHwuiDraw(mHwuiRenderer);
}
renderproxy->syncAndDrawFrame()
frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_Surface.cpp
static const JNINativeMethod gSurfaceMethods[] = {
{"nHwuiDraw", "(J)V", (void*) hwui::draw },
}
static void draw(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jlong rendererPtr) {
RenderProxy* proxy = reinterpret_cast<RenderProxy*>(rendererPtr);
nsecs_t vsync = systemTime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC);
UiFrameInfoBuilder(proxy->frameInfo())
.setVsync(vsync, vsync)
.addFlag(FrameInfoFlags::SurfaceCanvas);
proxy->syncAndDrawFrame();
}
unlockSwCanvasAndPost
private void unlockSwCanvasAndPost(Canvas canvas) {
nativeUnlockCanvasAndPost(mLockedObject, canvas);
}