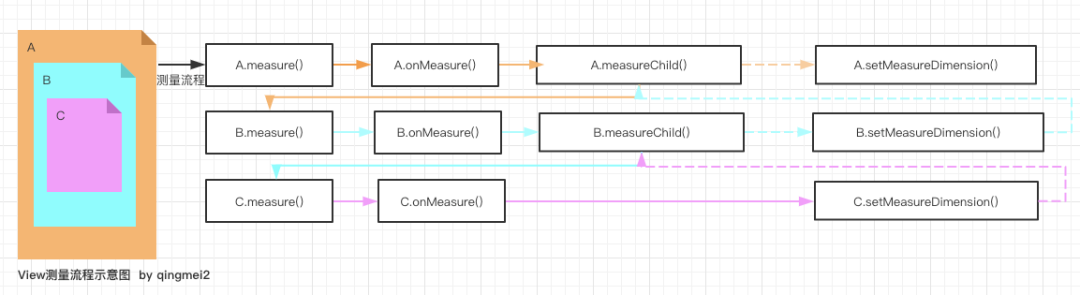
measure
原理总结
MeasureSpec
MeasureSpec是View的内部类,内部封装了View的规格尺寸,以及View的宽高信息。在Measure的流程中,系统会将View的LayoutParams根据父容器是施加的规则转换为MeasureSpec,然后在onMeasure()方法中具体确定控件的宽高信息。源码及分析如下所示:
public static class MeasureSpec {
//int类型占4个字节,其中高2位表示尺寸测量模式,低30位表示具体的宽高信息
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
/** @hide */
@IntDef({UNSPECIFIED, EXACTLY, AT_MOST})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface MeasureSpecMode {}
//如下所示是MeasureSpec中的三种模式:UNSPECIFIED、EXACTLY、AT_MOST
/**
* Measure specification mode: The parent has not imposed any constraint
* on the child. It can be whatever size it wants.
*/
public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The parent has determined an exact size
* for the child. The child is going to be given those bounds regardless
* of how big it wants to be.
*/
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The child can be as large as it wants up
* to the specified size.
*/
public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
}
UNSPECIFIED = 0
EXACTLY = 1073741824
AT_MOST = -2147483648
MATCH_PARENT = -1
WRAP_CONTENT = -2
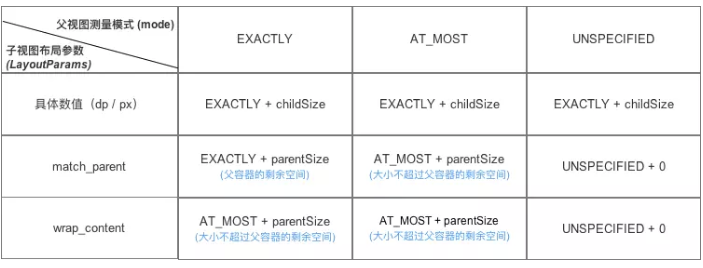
MeasureSpec的常量中指定了两种内容,一种为尺寸模式,一种为具体的宽高信息。其中高2位表示尺寸测量模式,低30位表示具体的宽高信息。
尺寸测量模式有如下三种:
①UNSPECIFIED:未指定模式,父容器不限制View的大小,一般用于系统内部的测量
②AT_MOST:最大模式,对应于在xml文件中指定控件大小为wrap_content属性,子View的最终大小是父View指定的大小值,并且子View的大小不能大于这个值
③EXACTLY :精确模式,对应于在xml文件中指定控件为match_parent属性或者是具体的数值,父容器测量出View所需的具体大小
对于每一个View,都持有一个MeasureSpec,MeasureSpec保存了该View的尺寸测量模式以及具体的宽高信息,MeasureSpec受自身的LayoutParams和父容器的MeasureSpec共同影响。
每个ViewGroup或View的onMeasure方法中的两个参数MeasureSpec,都保存了该view自身LayoutParams和父容器MeasureSpec共同影响之后提供的Measure mode和size信息
Measure过程中会传递MeasureSpec对象,包含mode和size信息,之后计算完毕后通过setMeasuredDimension设置到mMeasuredWidth和mMeasuredHeight(此时就只有具体的size信息了),之后在layout过程中可以拿到Measure好的宽高size进行摆放
ViewRootImpl Measure
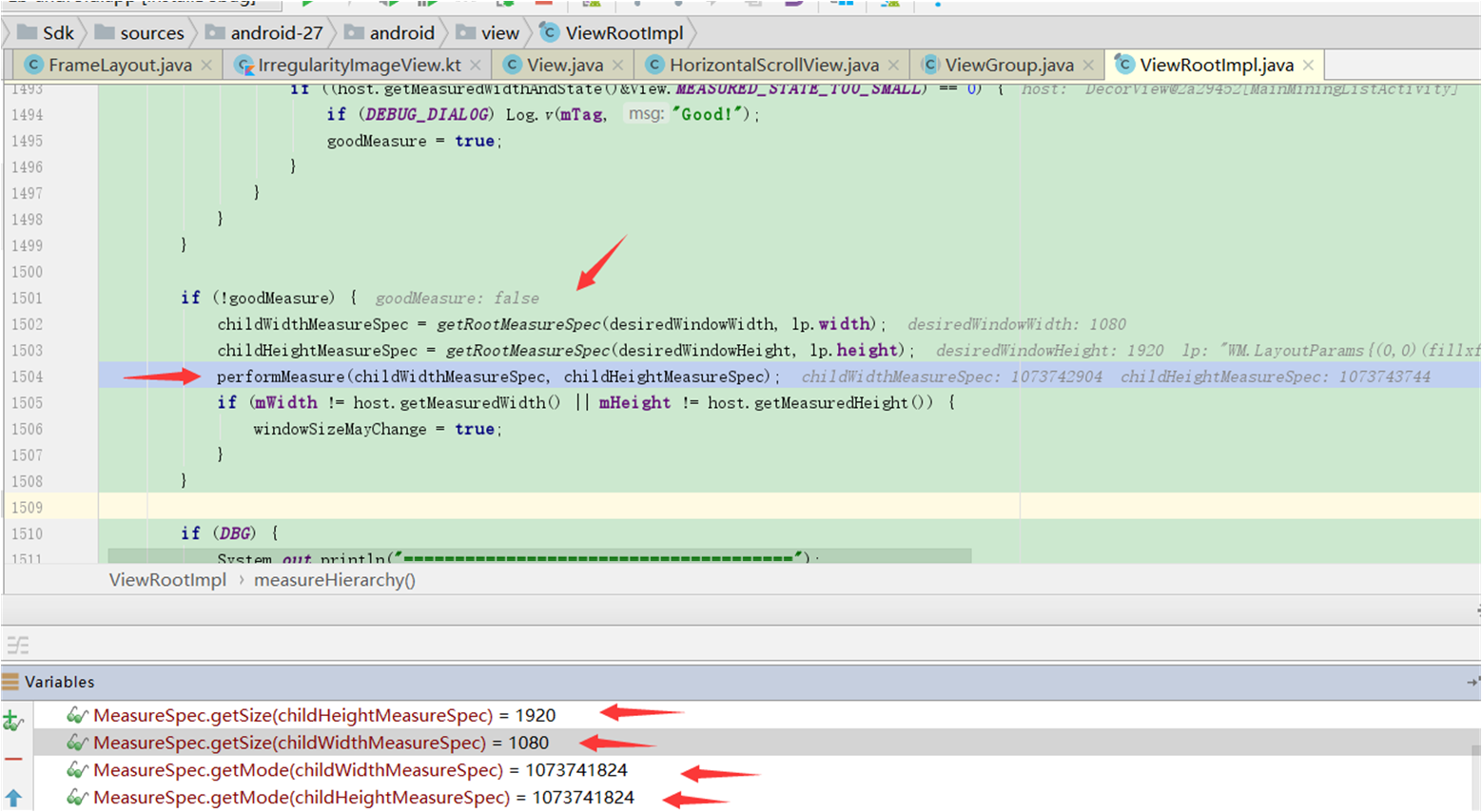
private boolean measureHierarchy(final View host, final WindowManager.LayoutParams lp,
final Resources res, final int desiredWindowWidth, final int desiredWindowHeight) {
int childWidthMeasureSpec;
int childHeightMeasureSpec;
...
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowWidth, lp.width);
childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
/**
\* Figures out the measure spec for the root view in a window based on it's layout params.
*
\* @param windowSize The available width or height of the window
\* @param rootDimension The layout params for one dimension (width or height) of the window.
\* @return The measure spec to use to measure the root view.
*/
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
// Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
// Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
}
ViewGroup Measure
ViewGroup::getChildMeasureSpec
View:setMeasuredDimension
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 1.通过遍历,对每个child进行测量
for(int i = 0 ; i < getChildCount() ; i++){
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 2.计算新的布局要求,并对子控件进行测量
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
// 3.完成子控件的测量,对高度进行累加
int height = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < getChildCount() ; i++){
height += child.getMeasuredHeight();
}
// 4.完成LinearLayout的测量
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
// 获取子元素的布局参数
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
// 通过padding值,计算出子控件的布局要求
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
// 将新的布局要求传入measure方法,完成子控件的测量
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
/**
\* Does the hard part of measureChildren: figuring out the MeasureSpec to
\* pass to a particular child. This method figures out the right MeasureSpec
\* for one dimension (height or width) of one child view.
*
\* The goal is to combine information from our MeasureSpec with the
\* LayoutParams of the child to get the best possible results. For example,
\* if the this view knows its size (because its MeasureSpec has a mode of
\* EXACTLY), and the child has indicated in its LayoutParams that it wants
\* to be the same size as the parent, the parent should ask the child to
\* layout given an exact size.
*
\* @param spec The requirements for this view
\* @param padding The padding of this view for the current dimension and
\* margins, if applicable
\* @param childDimension How big the child wants to be in the current
\* dimension
\* @return a MeasureSpec integer for the child
*/
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
//获取父View的测量模式
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
//获取父View的测量大小
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
//父View计算出的子View的大小,子View不一定用这个值
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
//声明变量用来保存实际计算的到的子View的size和mode即大小和模式
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
//如果父容器的模式是Exactly即确定的大小
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
//子View的高度或宽度>0说明其实一个确切的值,因为match_parent和wrap_content的值是<0的
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
//子View的高度或宽度为match_parent
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;//将size即父View的大小减去边距值所得到的值赋值给resultSize
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;//指定子View的测量模式为EXACTLY
//子View的高度或宽度为wrap_content
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;//将size赋值给result
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;//指定子View的测量模式为AT_MOST
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
//如果父容器的测量模式是AT_MOST
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
// 因为父View的大小是受到限制值的限制,所以子View的大小也应该受到父容器的限制并且不能超过父View
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
//如果父容器的测量模式是UNSPECIFIED即父容器的大小未受限制
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
//如果自View的宽和高是一个精确的值
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
//子View的大小为精确值
resultSize = childDimension;
//测量的模式为EXACTLY
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
//子View的宽或高为match_parent
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should be
//因为父View的大小是未定的,所以子View的大小也是未定的
resultSize = 0;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how big it should be
resultSize = 0;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
//根据resultSize和resultMode调用makeMeasureSpec方法得到测量要求,并将其作为返回值
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
View Measure
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// ... 公共逻辑
// 开发者需要自己重写onMeasure函数,以自定义测量逻辑
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 普遍意义上,setMeasuredDimension()标志着测量结束
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
// 宽度的默认值
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
// 根据不同的测量模式,返回的测量结果不同
switch (specMode) {
// 任意模式,宽度为默认值
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
// match_parent、wrap_content则返回布局要求中的size值
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
// measuredWidth 测量结果,View的宽度
// measuredHeight 测量结果,View的高度
// 省略其它代码...
// 该方法的本质就是将测量结果存起来,以便后续的layout和draw流程中获取控件的宽高
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
}